Life Part 3/4 - Pivotal points in the evolution of life.
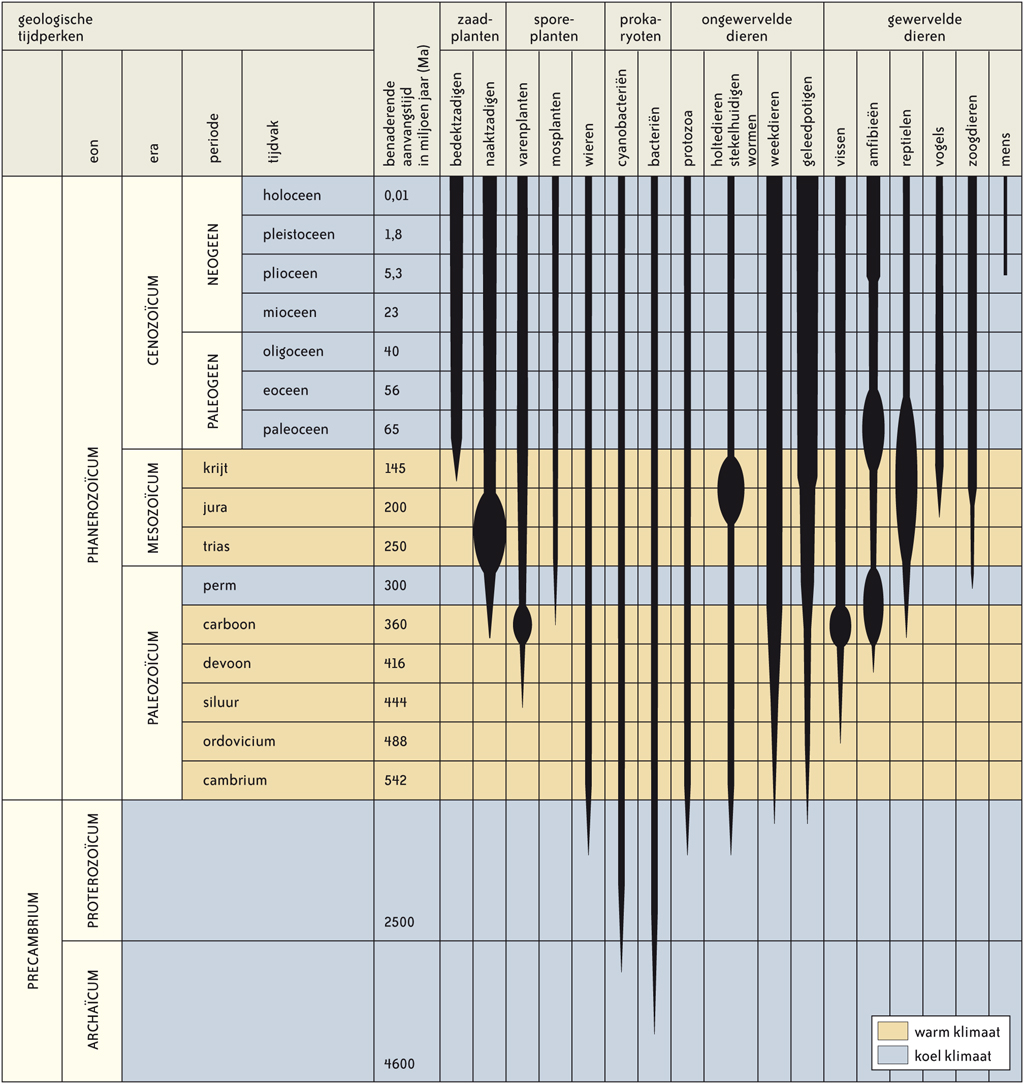
One tipping point follows another. It is a house of cards, one failure causes the entire system to collapse. We go over the so-called geological times determined by the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS).
Precambrian > 4600-542 million years ago.
The newly formed earth must first cool down with water vapor condensing into the oceans, this process takes about 1000 million years.
3500 million years ago, the so-called primordial soup is a fact. It is a fickle brew where the oldest fossil bacteria occur. Their core is simple and one speaks of prokaryotes.
2600 million years ago, these bacteria also occur on land, but this is a sidetrack. The majority stays in the water and evolves:
- For example, they contain chlorophyll a little later (green bacteria).
- They cohabit together to form the first multicellular organisms.
- And the very first photosynthesis takes place.
1700 million years ago the first eukaryotes occur, they have a modern nucleus with genetic material. Gradually there are algae, protozoa, sponges and cavity animals.
Cambrian > 542-488 million years ago.
There is an explosion of life.
Especially the seaweeds are doing extremely well, the primordial soup looks green.
In a relatively short time, all strains of the invertebrates arise. We get flatworms, round worms, rotifers, echinoderms, articulated worms, mollusks and arthropods. The oldest arthropods, the trilobites, still occur today.
The organisms without an external skeleton can do their gas exchange by simple diffusion. The organisms with an external skeleton develop gills for their gas exchange.
Ordovician > 488-443 million years ago.
The Ordovician was a period with a relatively warm climate and a high sea level. Life still takes place mainly in the water:
- The squid are flourishing, they are not cuties. They install the system of hunter and prey.
- The first vertebrates such as the jawless fish appear. Of these organisms, the or lampreys remain today.
Silurian > 443-416 million years ago.
Now the first plants appear on the land, probably in the tidal zone. They develop:
- Supporting tissue to stay upright.
- Vascular bundles to bring water from the roots to the leaves. With their roots, they can penetrate deeper and deeper into the land.
Devonian > 416-360 million years ago.
The sea level drops spectacularly and there are drought periods. Now comes a wide variety of cartilaginous fish:
- Important are the lungfish. In addition to gills, they also develop lungs. This allows them to survive a drought. For their reproduction they have to go back to the water and that is probably how the first amphibians arise.
- There are also the brush fins, the best known example is the current coelacanth. His fins for swimming in the water will later be transformed into fins (legs) to crawl on land.
On land, the giant horsetails and ferns arise. They are both spore plants that need moisture for their reproduction. The earth is covered with the first forests, the land sees green.
Carboniferous > 360-300 million years ago.
It’s warm on earth. More and more animals are migrating from the water to the land. Their external armor protects against dehydration, In addition to lung-like structures, trachea tubes arise as in the insects and spiders. Both groups flourish, giant insects manage to fly in the air, it would be no fun for humans.
The amphibians begin to lay eggs with a kind of leather shell. From now on they can reproduce on the land and that is how we arrive at the first reptiles.
The first seed plants appear, they are nudibranchs who carry their seeds virtually unprotected. Together with the ferns, they are at the origin of the fossil fuels on our planet.
Perm > 300-250 million years ago.
A cool period is coming, ice caps cover the land. The ice-free land areas around the equator remain covered with spore plants and nudibranchs.
But a mass extinction is taking place in which many species disappear forever:
- It’s just too cold, The animals with a changing body temperature can’t get going.
- Sea levels are falling to the current record level, large areas are frozen.
- The earth’s interior needs to let off steam and there is strong volcanic activity.
Triassic > 250-200 million years ago.
It gets warm again on earth. The nudibranchs are still doing well. The first pines arise, they already carry their seeds a little better protected in a cone.
The reptiles develop extremely strongly on the mainland. They begin to take on enormous proportions and learn to fly. Their brains remain extraordinarily small in relation to their size. There are benign herbivores and terrible predators.
A branch of the reptiles evolves in the direction of the mammals. They remain small but their warm-blooded household is an unprecedented advantage.
Jurassic > 200-145 million years ago.
This is the flowering period of the dinosaurs, these giant reptiles rule the earth.
At the end of the Jurassic, the primal bird Archaeopteryx appears. In addition to characteristics of the reptiles, we also find characteristics of the later birds.
Cretaceous > 145-66 million years ago.
Once again, the climate becomes cooler and drier. The very first nudibranch plants are having a hard time, the conifers are better armed against this change. Now comes the time of modern flowering plants, huge forests of deciduous trees cover the earth.
Shorter ice ages are starting, the giant reptiles are having a hard time. For the herbivores there is a threat of a food shortage. And 65 million years ago, a huge asteroid impact was fatal to them, they suddenly disappear from the face of the earth.
The small mammals seize their chance. Because of their warm-blooded system (a very expensive joke) they can come to the fore. Many new species are emerging, many survive in slightly modified form to this day.
The birds are also present. They have also opted for the warm-blooded system and derive indispensable benefit from it.
Today > 66-0 million years ago.
After the Cretaceous there are no more spectacular changes in the plants and the animals, they do evolve, but that is rather small:
- From the primates come the first hominids, the last 4 million years will be needed to come to modern man.
- Some mammals return to the water, the whales are the best known example.
- Also, some mammals learn to fly.
This illustration can be seen on the Wikipedia website.





Comments